As you may know, I’m using MySQL exclusively on GNU/Linux. To be honest for me it’s almos 20 years that the year of Linux on the desktop happened. And I’m very happy with that.
But this week-end, I got a comment on an previous post about upgrading to MySQL 8.0, asking how to proceed on Windows. And in fact, I had no idea !
So I spent some time to install a Windows VM and for the very first time, MySQL on Windows !
The goal was to describe how to upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0.
So once MySQL 5.7 was installed (using MySQL Installer), I created some data using MySQL Shell:
Of course I used latest MySQL Shell, 8.0.18 in this case. Don’t forget that if you are using MySQL Shell or MySQL Router, you must always use the latest 8.0 version even with MySQL 5.7.
Before upgrading, I ran MySQL Upgrade Checker to be sure everything is compatible with MySQL 8.0:
No problem, I’m good to go !
Don’t forget, now it’s the right time to perform a backup or a snapshot.
The first step is to stop the MySQL Service:
When done, you have to launch once again the MySQL Installer and use Modify your MySQL 5.7 Server product features to only leave the Sever data files checked:
When all is proceeded, you return to the MySQL Installer Product Overview and you Add a new product:
We select the latest MySQL 8.0 and there is no need to select Server data files, as we will upgrade our current data:
When is done, please stop the new MySQL80 service and modify the my.ini (of MySQL 8.0!) that is located in System\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0 by default:

In that file, we modify the actual value of datadir and we point it to where was located the datadir of MySQL 5.7. In this example I only used the default values:
And now it’s the most tricky part of the upgrade process, when you save this file, you must specified the ANSI encoding:

If you don’t use the right encoding, when you will start the MySQL Service, in the error log you will have a message like this:
[ERROR] Found option without preceding group in config file ... at line 1
When saved, you can start the service. It will take some times as MySQL will proceed to the upgrade of the system tables and other files as you can see in the error log:
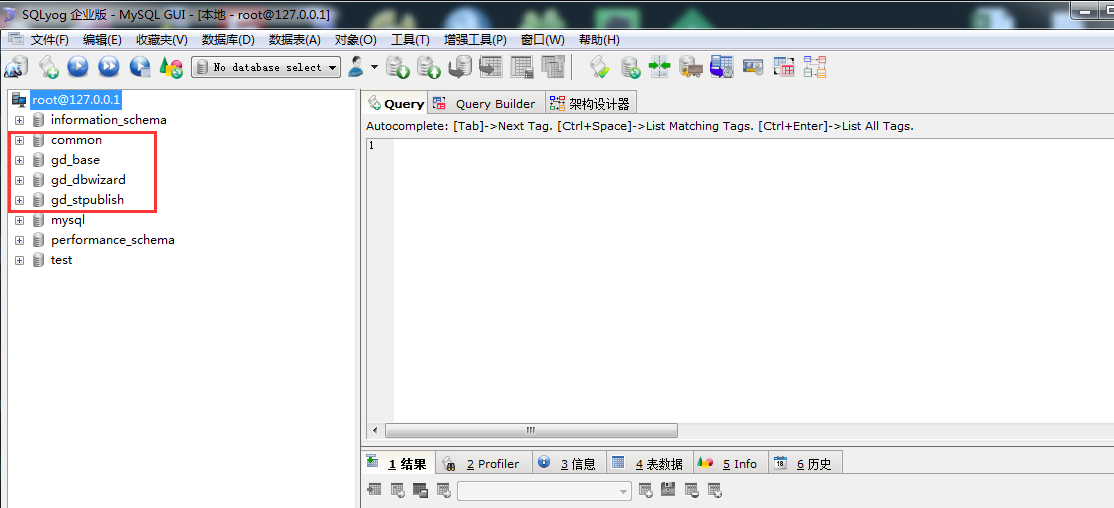
When the service is running again, you can connect and you should have access to all the data that was in you previous MySQL 5.7:

As you can see the test schema is there and of course we can check the content too:

I hope this post answers the questions of those that were experiencing issues when trying to perform an in-place upgrade from MySQL 5.7 to MySQL 8.0 in Microsoft Windows.

 English
English
 中文
中文